Insurance companies are on the hunt for third-party data that can help them improve the underwriting process, create a better overall customer experience, and enable the advanced analytics and predictive modeling needed to boost their decision-making capabilities.
Location data can help do just that – and so much more.
Here’s a quick look at how you can blend Foursquare Places data (aka point of interest data) with first-party data using the AWS Data Exchange and Atscale’s Virtual Semantic Layer to gain a more holistic view of the customer.
USING AWS DATA EXCHANGE AND FOURSQUARE PLACES
While the value of third-party is undeniable, it can be challenging to converge data sets that are fragmented across a data ecosystem. AWS Data Exchange and other platforms solve this problem by consolidating data from hundreds of third-party providers, such as Foursquare, into a centralized service.
Insurance providers can access Foursquare’s Places data via AWS Data Exchange to make smarter decisions about customer policies and more. Places, or point of interest (POI), data provides firmographic details such as venue names, addresses, and categories, as well as rich content attributes (such as photos, reviews, and tips). Foursquare Places encompasses 100+ million POIs globally, across 200 countries and 50 territories, and 900+ venue categories. In addition, the Visits feed includes data on where customers go in the real world, by tapping into a 100M+ user panel in 15+ countries.
Here are just two examples of ways that insurance companies can use analysis-ready location data like Places to gain a competitive edge:
1. IMPROVING THE DIGITAL CUSTOMER EXPERIENCE IN INSURANCE.
Experience – it can make or break a customer relationship. Data-driven insights can make underwriting, claims, and other processes more efficient and effective.
In the past, many insurance providers were using proxies for risk management, such as credit scores, geographic and demographic data. Digital data, such as location-based services, are now used by insurers to assess risk. For example, to evaluate a business policy, an insurance provider might use Foursquare data to understand surrounding businesses and assess risk. Businesses can mitigate these risks by installing devices such as water level indicators or fire sprinklers to help avoid claims, which is all a part of initial policy pricing.
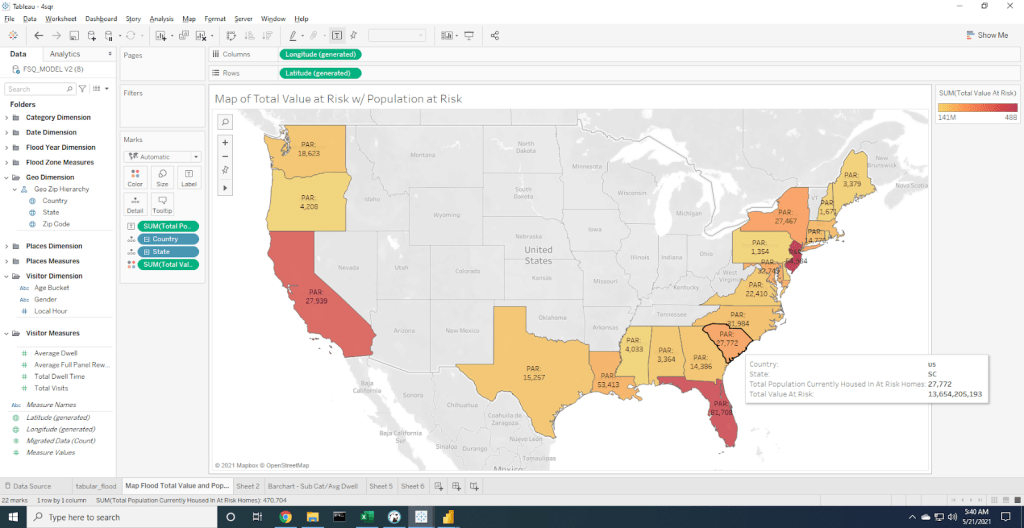
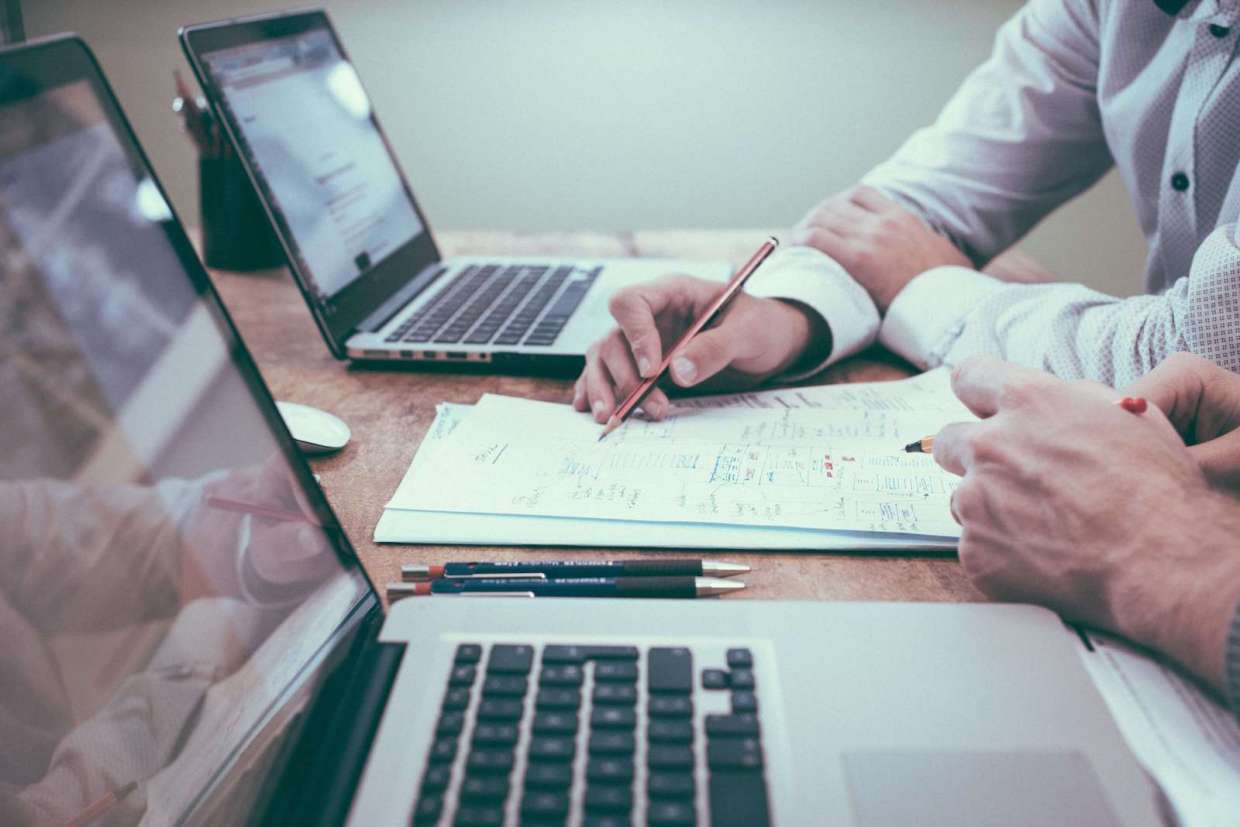
You can also incorporate user-generated photo imagery from Foursquare into existing data. For example, many carriers are looking to evolve to a continuous underwriting process to validate assumptions they made when they originally priced the policy, and see what may have changed. During the COVID-19 pandemic, these insights were particularly useful to businesses that had to adjust their business operating procedures – for example, restaurants installing heat lamps and tents outside to service guests. The proximity of these new hazards to existing risks may impact the pricing of a policy. These types of data, combined with existing legacy data such as flood zoning and fire risk maps, can prove impactful when mapping topography and determining the final risk for businesses, homeowners and more.
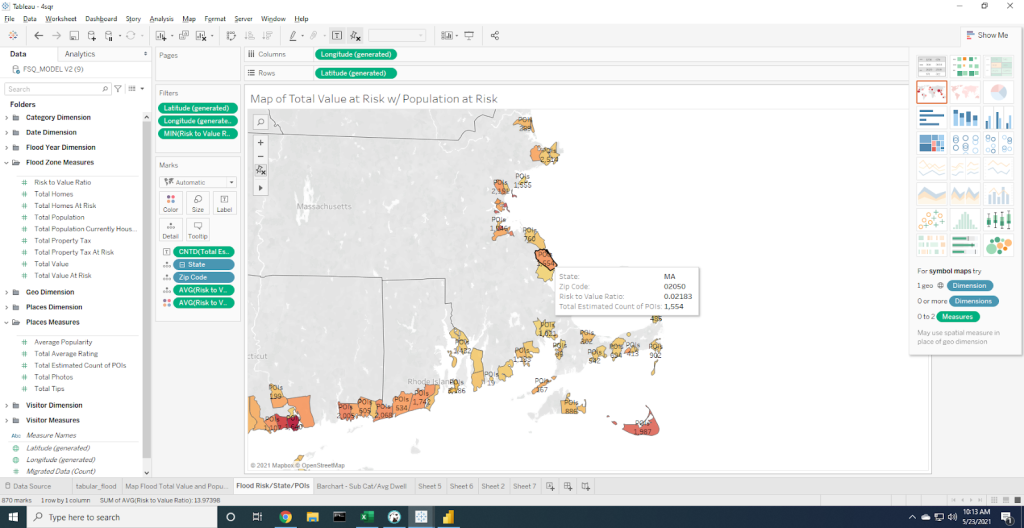
2. LEVERAGING ATSCALE TO BLEND FIRST- AND THIRD-PARTY DATA
Another key challenge insurance companies likely face is the fact that their data lives across legacy systems, SaaS applications, and marketplaces such as AWS Data Exchange – each with their own data schemas. As such, it’s important to use a modeling tool – such as AtScale’s Design Center – to provide a business centric semantic layer that can break down internal data silos and make external data analysis-ready. This allows you to model the data correctly and conduct effective analysis.
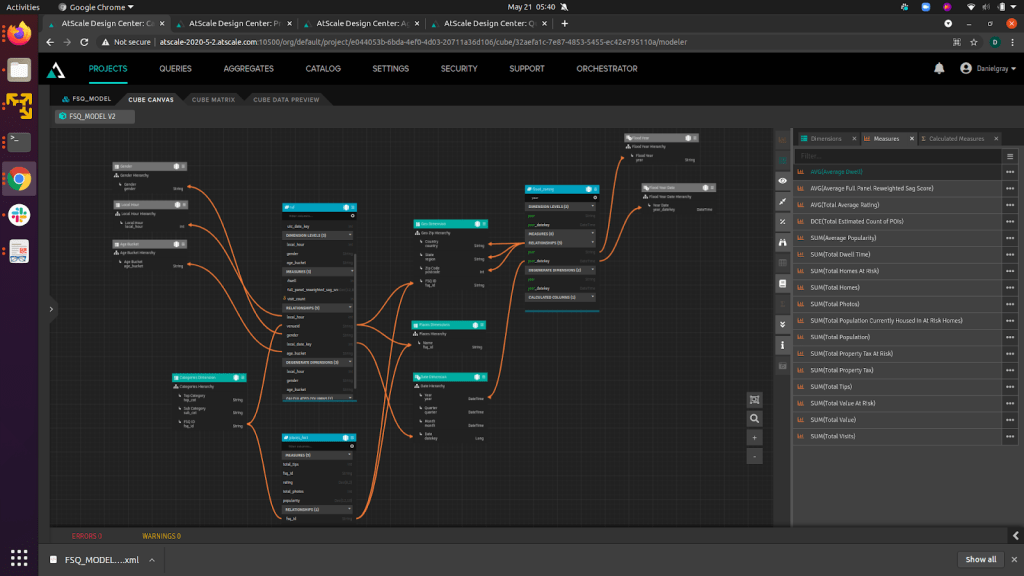
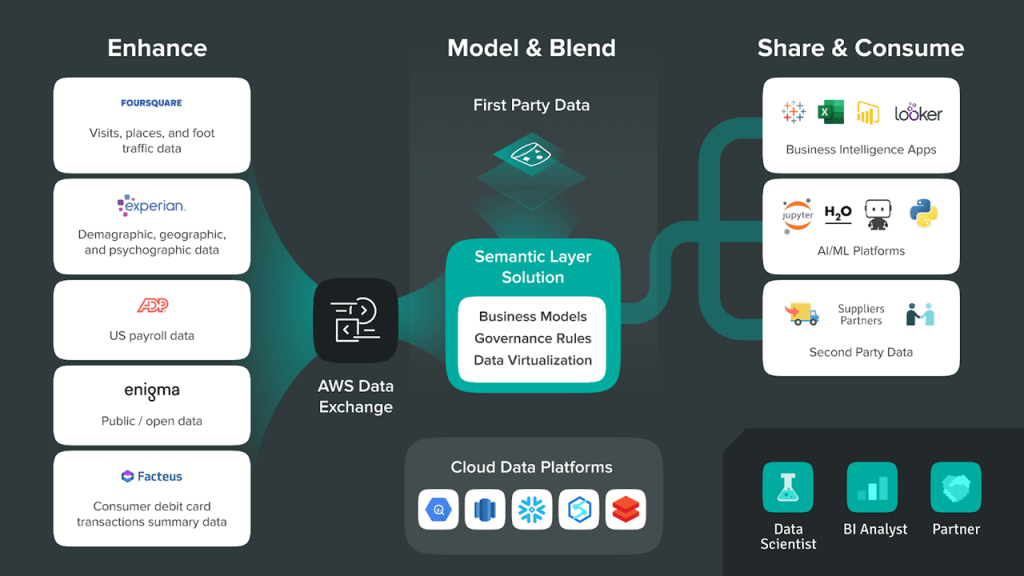
Additionally, a virtual semantic layer enables companies to share third-party data throughout the organization without expensive and time-consuming data movement and transformations. Indeed, data virtualization makes it easy for business analysts and data scientists to consume blended datasets within popular BI (e.g. Power BI, Tableau, Excel) and AI/ML tools (DataRobot, H2O, Python).
The value of first + third party data is only going to increase, and insurance companies have an incredible opportunity to use that augmented data to enable smarter real-time decisions that create better customer experiences and so much more.
Want to check out Foursquare Places & Visits premodeled data for yourself? Request a free trial here or check out a free demo here.
*Interested in learning more about how to put location data to work for your company? Reach out using the form below. *
