In the complicated world of geospatial data, analytics, and artificial intelligence, you may be wondering… how do I keep up? Let’s unpack some key concepts and commonly faced questions to clarify what these buzzwords really mean, the relationship between them, and how they’re making an impact across industries.
Q: What is the difference between “geospatial” and “geographic information systems (GIS)”?
You may hear people using the terms “geospatial” and “GIS” interchangeably, and while there is some overlap between the two as they both have a geographic component, they are distinct concepts with key differences.
“Geospatial” is the broad umbrella term that encompasses all spatially-related data, technology, and concepts.
“GIS” is a specific type of geospatial technology that falls under the geospatial umbrella. It is a computer system designed to work with geospatial data, providing the tools and functionality needed to store, analyze, and map spatial information effectively.
In other words, while all components of GIS represent geospatial technology, not all geospatial technology falls under the category of GIS. For example, other geospatial technologies that don’t fall under GIS include remote sensing, GPS devices, and geospatial data visualization tools.
Take this real-world example of how these concepts can be discussed together: To optimize store locations, retailers use GIS to map and analyze geospatial data, such as traffic patterns and competitor locations, which helps them make informed site selection decisions.
Q: What is geospatial artificial intelligence (GeoAI)?
Geospatial artificial intelligence, Geospatial AI, or GeoAI is the combination of geospatial data, technology, and science with artificial intelligence (AI) techniques. GeoAI enhances the ability to analyze and interpret complex spatial data by integrating advanced AI methods, including machine learning and deep learning, with traditional geographic data.
GeoAI offers significant benefits for businesses, including:
- speeding up data processing and automating workflows to drive efficiency and cost savings;
- anticipating trends and future behaviors, improving strategic planning with predictive modeling and forecasting; and
- increasing the accuracy of spatial analyses, reducing human errors.
This technology is being increasingly adopted across industries—such as retail, transportation, real estate, insurance, government, and more—elevating a wide range of applications, from personalized marketing to smart city development and environmental management.
Q: What is the difference between GeoAI and geospatial analytics?
The key difference between GeoAI and geospatial analytics is that there is no AI component involved in geospatial analytics. This means that while both functions may conduct similar activities such as data mining, spatial analysis, and geospatial modeling, GeoAI distinguishes itself by incorporating advanced AI techniques to generate predictive insights, automate complex decision-making, and evolve with new information dynamically. In contrast, geospatial analytics primarily relies on traditional statistical and computational methods to understand spatial relationships and patterns, offering more static analysis and less adaptability to evolving data.
Another core feature of GeoAI is the use of advanced machine learning and deep learning models, which are integral to its functionality. These models enable GeoAI to process vast amounts of geospatial data, recognize complex patterns, and make predictions that traditional methods cannot easily achieve.
For example, with deep learning models, GeoAI can dynamically adjust pricing in real-time by monitoring competitor prices and local market conditions, or predict future shopping patterns by analyzing past purchases and location history. Geospatial analytics can identify trends in current market prices or shopping patterns, but making these adjustments and developing future predictions would typically be up to you.
Q: When would someone use geospatial analytics over GeoAI and vice versa?
The choice between geospatial analytics and GeoAI depends on the specific use case, and in many cases is not mutually exclusive. Geospatial analytics is ideal for more straightforward tasks that provide all the necessary insights without needing an AI component, like mapping, modeling, or visualizing data. These functions can all be done in ready-made tools like FSQ Studio. In contrast, GeoAI is better suited for more complex situations that require predictive modeling, real-time data processing, or automated decision-making.
In addition to use cases, other factors like cost, ease of use, and expertise also come into play. For many users, geospatial analytics tools are more user-friendly and accessible, requiring less technical expertise. Additionally, the lower complexity and cost of traditional methods make them suitable for smaller projects or organizations with limited budgets. If your business has the capability and the need, combining geospatial analytics with GeoAI allows you to leverage the strengths of both, leading to deeper insights and greater efficiency in your operations.
Q: What are examples of how geospatial analytics and GeoAI are used together?
Retailers might use geospatial analytics to visualize their current store locations and identify demographic patterns in different regions. These insights could then be fed into a GeoAI system to predict where future store locations should be based on anticipated population growth, economic trends, and customer behaviors.
CPG companies may use geospatial analytics to map out existing retail distribution routes and analyze market penetration across various regions. This data can then be integrated with GeoAI to help automate the real-time adjustment of supply chains to respond quickly to changes in market conditions or consumer preferences.
Dining chains could use geospatial analytics to track real-time customer foot traffic and sales performance at different locations. GeoAI could then process this data in real time to adjust marketing campaigns dynamically, such as promoting special offers during peak times or in response to sudden changes in customer flow.
Q: What is generative artificial intelligence (GenAI)
Generative AI is a subset of AI that focuses on creating new content, data, or solutions based on patterns and examples it has learned from existing data. GenAI can produce original and unique outputs such as text, images, music, or even complex data structures.
For example, GenAI could be used to create synthetic financial market data to simulate various trading scenarios, test algorithms, and perform risk assessments. A more common example that has risen in popularity is ChatGPT – a GenAI tool that leverages a language model to generate human-like text responses based on prompts.
Generative AI differs from other types of AI in that it generates new content or data, whereas other AI models primarily analyze existing data to recognize patterns, make predictions, or inform decisions without creating anything new.
Q: How can GenAI and GeoAI be integrated to enhance their capabilities for businesses?
The convergence of GenAI and GeoAI has unlocked new levels of productivity, creativity, and innovation. These technologies, particularly when combined, offer powerful tools and solutions tailored to the needs of different personas including marketers, developers, product teams, GIS specialists, and more.
For example:
- Marketers could leverage GenAI to create customized ad creatives based on the preferences of key audiences that GeoAI predicts have the highest likelihood of being influenced to visit your new store location.
- Product teams could use GeoAI to analyze purchasing trends and environmental factors to forecast product demand, while GenAI creates adaptive supply chain strategies or personalized product recommendations based on the forecast.
- Data analysts may employ GeoAI to forecast regional sales data trends, while GenAI generates detailed reports and visualizations to highlight key insights.
- Developers could use GenAI to write custom code for a consumer app that powers predictive models, automatically recommending restaurants to users based on past visits and preferences.
- GIS specialists can use GeoAI to analyze large datasets, such as satellite imagery, to detect land use changes and environmental shifts, and then use GenAI to automatically retrieve and organize relevant data points, generating detailed summaries and actionable insights.
Q: How do all these terms—Geospatial, GIS, GeoAI, and Generative AI—fit together?
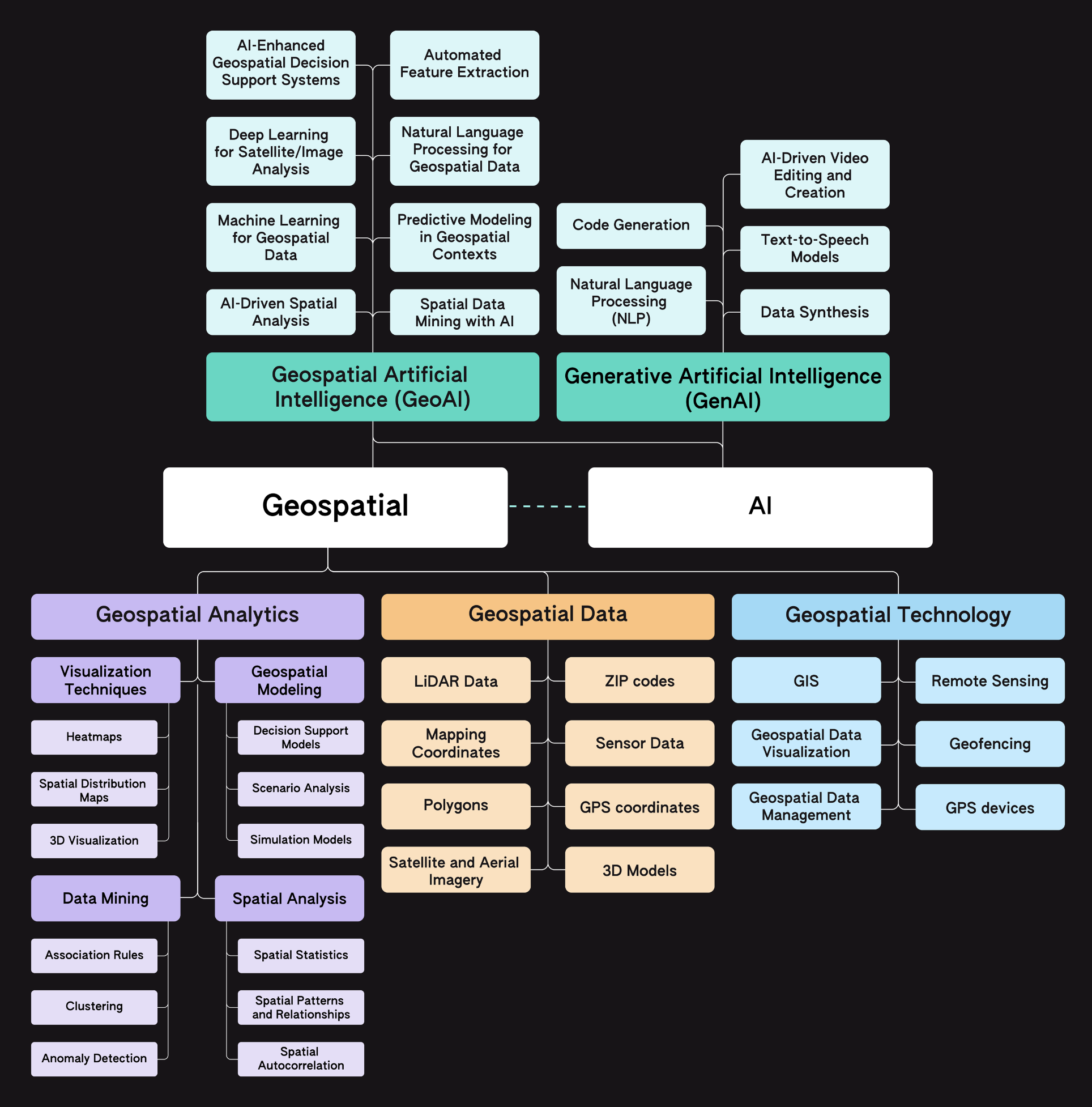
Geospatial, GIS, GeoAI, and Generative AI are interconnected elements in data analysis and AI. Together, they offer a complete toolkit for advanced spatial analysis and creative data applications.
Simply put, geospatial data, technology, analytics, and AI all work together to enhance spatial understanding and decision-making. Geospatial data provides the raw geographic information, while geospatial technology like GIS manages and visualizes this data. Geospatial analytics applies methods to analyze and uncover patterns, and Geospatial AI uses advanced AI techniques for predictive modeling and automation.
Generative AI is a complementary technology that extends these capabilities by creating new content or scenarios. While it operates outside the traditional geospatial framework, GenAI enhances the insights and solutions derived from geospatial analysis by generating innovative and synthetic outputs.
Q: What key roles and expertise are crucial for unlocking the full potential of GeoAI technology?
To fully leverage the capabilities of geospatial data, tech, AI, and its insights, businesses must ensure they have the right teams and partnerships in place.
In-House Expertise (Data Scientists, Analysts, GIS Specialists): The foundation of a successful internal geospatial strategy lies within a business’s in-house team, particularly data scientists, GIS specialists, and data analysts. These professionals are essential for developing, training, and refining geospatial and GeoAI models. Data scientists bring the technical skills required to create algorithms that process geospatial data, while GIS specialists add critical insights by understanding spatial relationships and how to best represent them in models. Data analysts then work to interpret the results, ensuring that the complex data processed by GeoAI is transformed into clear, actionable insights that can drive business decisions.
In-house teams also play a crucial role in continuously monitoring and updating these models to ensure they remain accurate and relevant as market conditions and consumer behaviors evolve. This internal expertise allows businesses to maintain a high level of control over their geospatial initiatives, ensuring that the insights generated are tailored to their specific needs and objectives.
External Partners: In addition, or as an alternative to building strong internal teams, organizations can also benefit from partnering with external providers who specialize in high-quality geospatial data and technologies. These external partners often have cutting-edge tools and expertise that can complement in-house efforts or provide more cost-effective solutions for teams lacking internal resources and looking for quick implementation turnarounds.
For instance, leading brands – such as Pinterest, Papa Murphy’s, and Reddit – partner with Foursquare to leverage GeoAI-driven marketing tools to accurately measure advertising campaign impact on incremental store visits.
Third-party partners may also already be integrating advanced techniques like GeoAI into their solutions for location-based marketing, risk assessment, or supply chain optimization. This allows businesses to leverage GeoAI’s benefits through their existing partners without needing to find a separate GeoAI provider. Additionally, these partners often offer ongoing support and updates, ensuring that the data, models, and technologies remain aligned with the latest advancements and best practices in the field.
If you’re curious if your partner is leveraging AI to build and maintain their products and services, just ask! Understanding how their technology works is crucial to trust the insights it provides.
The Road to Business Success with Geospatial Technologies & Expertise
Understanding key industry terms – like geospatial data, GIS, GeoAI, Generative AI, and more – enables you to confidently evaluate technology solutions, communicate effectively with experts, and make informed decisions that drive your business forward.
If you’re looking for a geospatial partner that leverages cutting-edge data science with a seasoned team of location experts, check out Foursquare’s suite of location intelligence solutions:
- Studio – Perform advanced analytics with big geospatial data and create compelling visualizations and maps;
- Audience – Build tailored audience segments based on real-world behavior;
- Proximity – Deploy custom geofences for precise location-based targeting;
- Attribution – Accurately measure campaign performance on in-store visits and purchases;
- Places API – Access global POI data via our API for real-time venue search, discovery, and ranking.
- Places Pro — Make data-driven decisions and build performant apps with FSQ’s comprehensive and dynamic POI dataset.
Curious to learn more about how Foursquare’s geospatial solutions can help your business succeed?
Authored by: Summer Slough