Since its launch, Kepler.gl has transformed how data scientists extract insights from location data, pioneering immersive visualization and interactive analysis directly in the browser. Built on deck.gl’s GPU-accelerated rendering, it has enabled teams to uncover patterns in millions of data points, from urban mobility flows to global supply chain networks. However, as datasets grow larger and analytical needs become more sophisticated, users have faced limitations with browser memory and complex spatial operations. Enterprise solutions such as Foursquare Studio have attempted to address these limitations by moving the computation to the cloud through connectors to data warehouses and on-demand tiling capabilities. While this approach serves large organizations effectively, it requires significant infrastructure investment and technical expertise, creating a barrier for many teams working with location data.
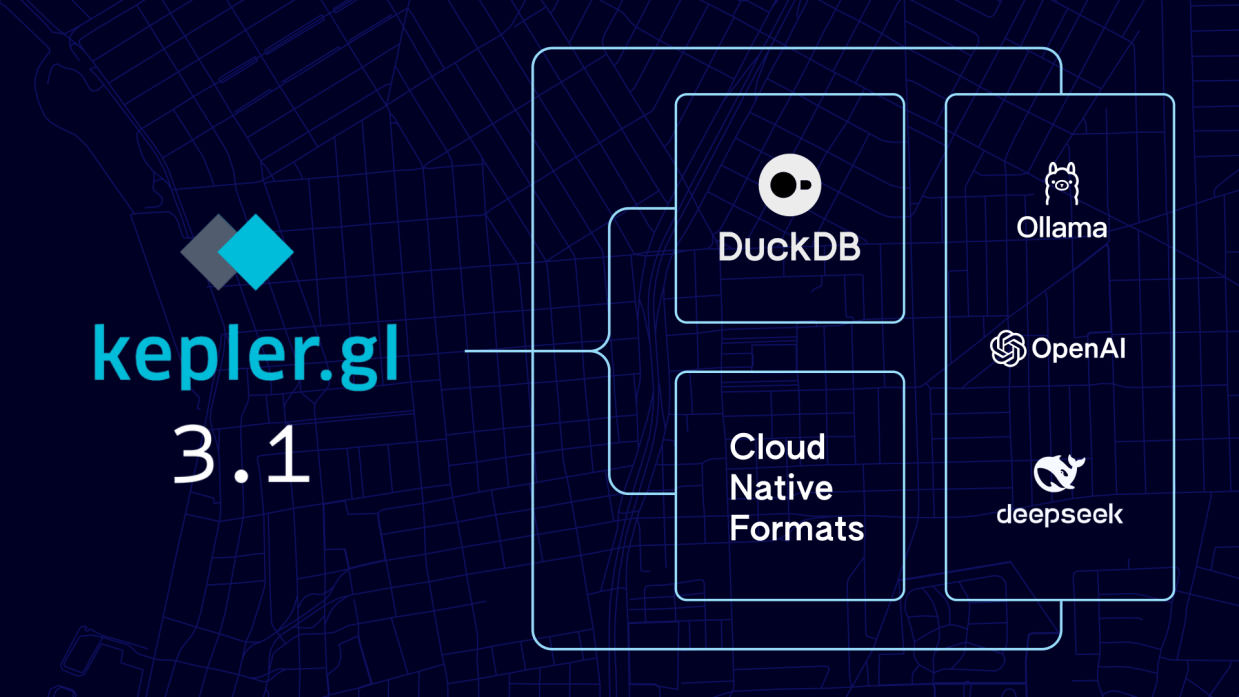
Today, we’re excited to introduce Kepler.gl 3.1, a groundbreaking release that brings enterprise-grade spatial analysis to your browser. Building upon the latest trends in geospatial technology, this update harnesses cloud-native data formats, generative AI, and edge computing to deliver a step-function change in analytical capabilities through three key innovations:
1. Embedded DuckDB Analytics Engine
By embedding DuckDB as our analytical engine within the browser, we enable efficient querying of data with SQL, including spatially partitioned GeoParquet files from cloud storage, without requiring a database connection. DuckDB’s spatial extension enables complex spatial queries by reading only relevant data partitions, eliminating the need to download entire datasets into browser memory.
2. Smart Map Rendering with PMTiles
Our implementation of vector tile rendering with PMTiles format redefines how you work with massive spatial datasets within Kepler. The technology dynamically loads only the data visible in your viewport, delivering enterprise-grade visualization capabilities without requiring server infrastructure.
3. AI-Powered Assistance
Through our partnership with with Center for Spatial Data Science at University of Chicago, we’re introducing an intelligent LLM assistant that bridges the gap between technical complexity and intuitive workflows. Whether you need to compare dwell times across neighborhoods or visualize customer hotspots, the assistant translates natural language into optimized queries and compelling visualizations, making advanced spatial analysis accessible to everyone on your team. You can choose between prominent enterprise LLMs from OpenAI, Google and DeepSeek, or a locally deployed model through Ollama.
Beyond our core innovations, Kepler.gl 3.1 introduces a suite of refinements that transform spatial data visualization and analysis. The platform now offers sophisticated color customization across categorical fields and aggregate layers, coupled with intelligent numeric formatting that adapts to your context – from financial metrics to percentage-based analyses. We’ve enhanced the analytical workflow with multi-provider base map support (Mapbox and MapLibre), advanced animation controls with filter synchronization, and extended layer support for GeoJSON and H3 hexagons. Complementing these capabilities are quality-of-life improvements including one-click layer zoom, customizable legends, and enhanced timeline controls, all optimized for performance with large-scale datasets. Together, these features create a more powerful yet accessible platform for transforming complex spatial data into actionable insights.
This evolution of Kepler.gl marks a pivotal moment in democratizing location intelligence, making powerful geospatial analysis accessible directly through the browser. For data scientists, analysts, and researchers, this represents a fundamental shift in how teams can explore and derive insights from location data.
Check out our detailed release notes here.
Try the new Kepler features
Contributors: Shan He, Ilya Boyandin, Igor Dykhta Fabion Kauker Devin DiStefano